By Offerings
- Direct Metal Printing
-
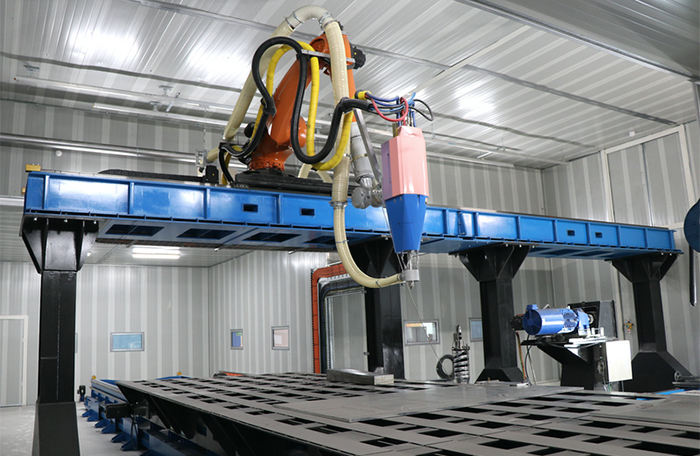
Direct Metal Printing (DMP) technology is developed in such a way, it gives you complete freedom to design, test and manufacture stronger 3D printed metal parts that are light, durable which cannot simply be possible with standard manufacturing.
Benefits of Metal Printing:
- Lightweighting
- Part consolidation
- Fluid Flow
- Functional Improvement
- Selective Laser Sintering
-
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is the rapid prototyping technology that uses a laser to harden and bond small grains of plastic, ceramic, glass, metal or other materials into layers in a 3 dimensional structure.
Considering its robustness and capability to produce complex whole parts, SLS can bring major time and cost benefits for small-run parts that would usually require some assembly with traditional manufacturing.
- Stereolithography
-
Stereolithography (SLA) uses an ultraviolet laser to precisely cure photopolymer cross-sections, transforming them from liquid to solid. Parts are built directly from CAD data, layer-by-layer into prototypes, investment casting patterns, tools, and end-use parts.
- MultiJet Printing
-
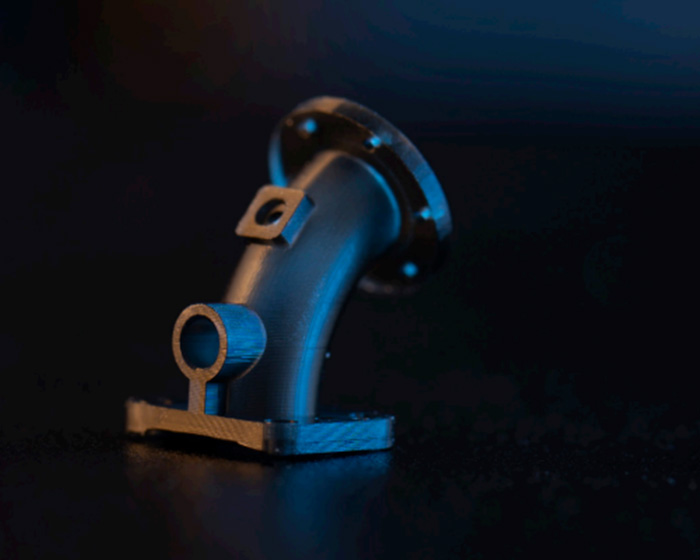
MultiJet Printing is a material jetting printing process that uses piezo printhead technology to deposit materials layer-by-layer. These high-resolution 3D printers use a separate, meltable or dissolvable support material that can be completely removed in a virtually hands-free process, allowing even the most delicate and complex features to be thoroughly cleaned without damage.
- Digital Light Processing
-
DLP (Digital Light Processing) is a 3D printing process that works with photopolymers and uses a more conventional light source, such as an arc lamp with a liquid crystal display panel, which is applied to the entire surface of the vat of photopolymer resin in a single pass.
DLP produces highly accurate parts with excellent resolution and only a shallow vat of resin is required to facilitate the process, which generally results in less waste and lower running costs.
- Ceramic Stereolithography
-
Ceramic stereolithography (CSL) is a precise and high-resolution additive manufacturing (AM) technique to fabricate complex ceramic parts. In CSL, conventional raw resins are loaded with ceramic powders acting as fillers, and the ceramic-loaded resins are typically called ceramic resins. CSL process consists of these main steps: preparing a suitable photocurable ceramic suspension, the building of the ceramic part, de-binding, and sintering.
- Titomic Kinetic Fusion
-
Titomic Kinetic Fusion (TKF) utilizes the supersonic particle deposition of metal powders to create industrial-scale parts and complex surface coatings with high-performance materials, including titanium, drastically increasing productivity by reducing costs and lead times from months to days. It also reduces waste by 80% compared to traditional machining through near-net-shape manufacturing. As the parts are manufactured, they are built to near their final shape, then precision machined to final tolerance, removing up to 5-10% of material.
- Projection Micro Stereolithography
-
Projection Micro Stereolithography (PµSL) - ULTRA-HIGH RESOLUTION, ACCURACY, AND PRECISION Boston Micro Fabrication is the world leader in micro-precision 3D printers utilizing Projection Micro Stereolithography (PµSL) technology.
- Fused Deposition Modelling
-
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is the rapid prototyping technology that uses a laser to harden and bond small grains of plastic, ceramic, glass, metal or other materials into layers in a 3 dimensional structure.
Considering its robustness and capability to produce complex whole parts, SLS can bring major time and cost benefits for small-run parts that would usually require some assembly with traditional manufacturing.